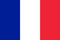
Prostatitis is an inflammatory process localized in the prostate.This pathology is quite common and is often diagnosed in men of childbearing age.The prostate (the second name for the prostate gland) is located under the bladder and partially surrounds the urinary tube (urethra).Therefore, even a minor dysfunction of this organ leads to dysfunction of the genitourinary system.
Causes of the development of prostatitis
Prostatitis is classified as an inflammatory process, but this does not mean that it is caused exclusively by pathogenic microorganisms.Doctors (andrologists deal with diseases of the male reproductive system) identify several reasons for the development of the pathology in question:
- Blood congestion in the pelvis.This refers to a violation of blood microcirculation in the prostate and neighboring organs, which provokes enlargement of the organ.A violation can occur against the background of a sedentary lifestyle, obesity (it does not have to be critical) or in the postoperative period.
- Infection of the urogenital system.Most often, when examining a patient with prostatitis, doctors isolate gonococci, staphylococci, chlamydia and trichomonas.Very rarely, an infection can penetrate the prostate against the background of a sore throat or flu - in this case, the respective inflammatory process is differentiated as a complication.
- Regular injury to the pelvic organs.For this reason, prostatitis develops in drivers - they are constantly stressed on the perineum, the prostate experiences tremors and vibrations.
- Penetration of bacteria through biological body fluids.In every human body, bacterial colonies live in the intestines and urethra.Under normal conditions they are absolutely harmless and only under favorable conditions (weakened immunity, long-term use of medications, chronic diseases, human immunodeficiency virus) do they become pathogenic and cause inflammatory processes.These bacteria can enter the prostate via the blood or lymph.
In addition, when diagnosing the inflammatory process in the prostate, glandular factors that serve as provocateurs of pathology can be taken into account:
- regular hypothermia – this may be due to the peculiarities of working conditions or non-observance of the rules for wearing clothes at certain times of the year;
- Dysfunction of the endocrine system - excessive or insufficient production of male hormones, diagnosed diabetes mellitus;
- too active sex life and prolonged abstinence – the prostate is exhausted;
- all chronic diseases - there are officially registered cases of the development of prostatitis against the background of untreated bronchitis, caries, cystitis and urological infections.
Symptoms of the inflammatory process
Andrologists distinguish between main and indirect signs of a developing inflammatory process in the prostate.The main symptoms are clearly expressed:
- Urination becomes more frequent regardless of the amount of fluid consumed;
- The immediate moment of urine outflow is painful, the man feels pain and burning in the urethra;
- The body temperature rises (hyperemia) to critical values.
These symptoms are quickly joined by a burning sensation throughout the perineum and pain during bowel movements.
Indirect signs of the inflammatory process in the prostate are not so noticeable, but men should not ignore them:
- ejaculation becomes too rapid – the time of sexual intercourse is shortened;
- The erection can be quite long at night;
- decreased libido – partial or complete;
- “Flakes” or white “threads” appear in the urine.
Please note: These indirect signs indicate the beginning of the development of the inflammatory process in question - it is easily treatable and proceeds without complications.
Prostatitis is divided into acute and chronic forms, each with its own symptoms.
Acute form of prostatitis
Acute prostatitis always begins suddenly and is manifested by:
- increased temperature;
- persistent pain in the perineum;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- Passing a very small amount of urine when the bladder feels full.
Please note: The most dangerous condition in the acute form of prostate inflammation is urinary retention.In this case, the man feels a strong desire to go to the toilet, but urine is not released even with strong exertion.Acute urinary retention is accompanied by severe pain in the area of the anatomical position of the bladder and a feeling of pressure - patients describe their condition as “the bladder is about to burst”.The condition requires immediate medical attention, which consists in the use of a catheter - it is inserted into the urethra and bladder and literally "squeezes apart" the swollen gland.As soon as the catheter reaches the bladder, urine outflow begins and the patient immediately feels relief, his condition returns to normal for a short time.
Chronic form of prostatitis
This type of pathology is practically asymptomatic - occasionally a man feels short-term pain in the perineum (similar to lumbago), notices changes during sexual intercourse - it can either lengthen or shorten.In addition, the patient becomes irritable, sleep becomes restless at night, the stream of urine may become weak (this is due to a narrowing of the urinary canal), and in the morning there may be white lumps in the urine in the form of flakes or threads.
Please note: The chronic form of the inflammatory process in the prostate can develop unnoticed by the patient.The fact is that acute prostatitis occurs at a young age with mild symptoms and if a young man is addicted to alcohol or is too passionate about work, he does not have time to pay attention to changes in urination or periodic pain in the perineum.The symptoms of acute prostatitis disappear over time, but this does not mean that the disease has regressed - it has simply become chronic.
Treatment methods for prostatitis
Treatment of the inflammatory process in the prostate should only be carried out under the supervision of an andrologist.He not only diagnoses prostatitis itself (often its symptoms are identical to prostate cancer), but also reveals the true cause of its occurrence.In general, several different therapy methods can be used to treat prostate inflammation.
Drug treatment
For prostatitis, antibacterial agents (antibiotics) can be prescribed, but only if during the examination pathogenic bacteria were isolated and identified as the cause of the development of the pathology.In addition to antibiotics, the patient is prescribed probiotics or prebiotics - drugs that normalize the intestinal microflora and counteract the development of pathological processes in it.
If the inflammatory process began due to the negative impact of external factors (hypothermia, injury), anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs are prescribed.
In case of hormonal disorders, a man must undergo hormone therapy.
Please note: Treatment with medication is very variable and must therefore be selected individually - self-medication is strictly prohibited in this case.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of prostate inflammation should be comprehensive.And against the background of taking medications, it will be effective to carry out certain physical procedures:
- Electrical stimulation accelerates metabolic processes, triggers more active hormone production and restores the structure of the gland.
- Magnetic therapy is a painless procedure that helps reduce the amount of inflammation and eliminate swelling of the prostate.
- Prostate massage – performed only after treatment of acute inflammation;The procedure is painful but very effective.
Traditional medicine
Please note: recipes from the category of traditional medicine should not be the only method of treatment - they can only speed up the therapeutic process and improve the effect of taking medications and performing physical procedures.
The most effective and safe methods of traditional treatment include:
- Eat pumpkin seeds.They contain zinc, which is an essential element for men's health.Therefore, with prostatitis, you need to eat 30 raw seeds 30 minutes before meals throughout the entire period of therapy.
- Pumpkin honey balls.Peel 100 grams of raw pumpkin seeds, grind them in a meat grinder (or in a blender, but not to fine crumbs) and mix them with 200 grams of honey.Roll small balls out of the resulting mixture and store in the refrigerator.Before eating (30 minutes before) you need to eat 1-2 balls - you don't need to chew it, it's better to dissolve it slowly.Treatment with this recipe continues until the symptoms of prostatitis disappear.
- Decoction of hazelnut leaves.You can collect hazelnut leaves yourself or buy dry raw materials at a pharmacy;There is a glass of boiling water per tablespoon of the starting material.The decoction is brewed like normal tea for 20 minutes, filtered and taken 50 ml at least 4 times a day.Please note: hazelnut bark is also sold in pharmacies - it can also be used to treat prostatitis according to the same recipe.However, keep in mind that the steeping time for bark is doubled.
- parsley juice.Prepare it from the green leaves of the plant and take 1 tablespoon three times a day before meals.
- Decoction of parsley seeds.You need to take 1 tablespoon of parsley seeds, pour 400 ml of boiling water and let stand for 2 hours (you can do this in a thermos).You need to take the decoction daily in the morning and evening in the amount of 1 tablespoon.
Regardless of how safe the product may seem, you should always consult your doctor first.For example, if a man suffers from cholelithiasis in addition to prostatitis, he is strictly prohibited from using pumpkin seeds - each prescription is strictly individual.
Diet and lifestyle

To achieve the best result in therapeutic measures against prostatitis, you must follow a certain diet.It should exclude fatty meats, smoked and overly salty foods, baked goods and chocolate from the diet.The menu includes fish and seafood, milk and dairy products, and steamed vegetables.With prostatitis, it is very useful to consume freshly prepared juices from vegetables and fruits - they help strengthen and restore the immune system.
During therapy, you need to give up alcohol and lead an active lifestyle - at least do morning exercises, walk more and get rid of extra pounds.
Prostatitis is not considered a life-threatening disease for men, but ignoring its symptoms can lead to the development of serious complications.One of the most serious consequences is male infertility and loss of erectile function, which often occurs with long-term chronic prostatitis.